Reproduction
It is a biological process by which new individuals are produced from their parent/s. There are two main types of reproduction:
Asexual reproduction: It is a method of reproduction in which one parent give rise to a genetically identical offspring.
Sexual reproduction: It is another method of reproduction in which male and female gamete cells combine to form genetically different offspring.
Bacteria
Bacteria are unicellular microorganisms. They belong to the prokaryotic group which means that they lack a true nucleus. The nucleic material of bacteria is found dispersed in the cytoplasm. They can be found in different shapes such as bacilli, cocci, and spiral.
Bacteria contain cell walls as an outer covering which is made up of peptidoglycan. They have a whip-like structure called flagella for movement. Several bacteria also have a short hair-like structure called pili. There are two types of pili present in bacteria i.e, fimbriae involved in attachment to surfaces and sex pili involved in sexual reproduction.
Reproduction method of bacteria
Bacteria reproduce by sexual as well as asexual reproduction. They produce their exact copy by asexual reproduction while sexual reproduction results in genetic variations in the daughter bacteria.
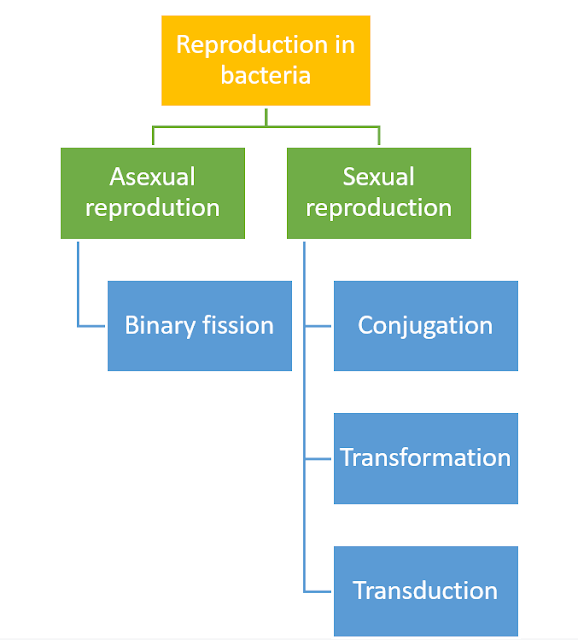
|
|
Reproduction Method of Bacteria |
Asexual reproduction in bacteria by binary fission
Bacteria reproduce asexually by binary fission. During binary fission, one cell of bacteria is divided into two new identical cells. The steps involved in binary fission are:
- Nucleic acid (DNA) of a bacterial cell is replicated.
- The cell grows and elongates in size.
- Both DNA starts to distance from each other and moved to opposite sides.
- Once the bacterial cell reaches double its original size, the cell membrane starts to squeeze inward from the middle.
- Cell wall is formed at the squeezed point which separates both DNA molecules.
- Finally, both cells are separated from each other into two identical bacterial daughter cells.

|
|
Asexual reproduction in bacteria by binary fission. Figure created in
BioRender.com |
Advantages of binary fission
Binary fission is beneficial to bacteria in many ways such as:
- It allows bacteria to produce a large number of cells in a short period. One typical cell of bacteria, under optimum conditions, is divided into two cells in 20 minutes. This property of bacteria is highly used in biotechnology to acquire recombinants produces in a short period.
- Binary fission produces genetically identical cells. So, the beneficial characteristics of a parent bacterium are transferred to daughter cells as such and help their survival.
- No time is wasted in search of a mate as one parent is involved in binary fission.
Disadvantages of binary fission
Along with the many benefits of binary fission, this method is not without any drawbacks. One major disadvantage of binary fission is that the species cannot survive the changes in its habitat since there is no genetic recombination, and the entire population might eliminate.
Video lesson
Sexual reproduction in bacteria
Sexual reproduction in bacteria does not involve male and female gametes and their fusion to form zygotes as observed in eukaryotes. Even yet, some mechanisms are similar to sexual reproduction, or perhaps we should say a primitive kind of sexual reproduction, in which DNA is exchanged between two bacteria.
These methods allow bacteria to make changes in genetic material to survive a particular environment by making genetic recombination. The methods found in bacteria through which the exchange of genetic material takes place are:
- Conjugation
- Transformation
- Transduction
1. Conjugation
It is a method of sexual reproduction in bacteria in which two bacteria exchange their genetic material through direct contact. The bacteria that provides genetic material is called donor bacterium, while the bacteria that get the genetic material is known as recipient bacterium. The steps involved in the conjugation process are:
- The donor cell will recognize the recipient cell and will move closer to it.
- The connection is established between two bacteria with the help of sex pilus.
- The single-stranded circular DNA (F plasmid) is transferred to the recipient bacterium through the established connection.
- The connection between two bacteria is disrupted after the exchange of genetic material.
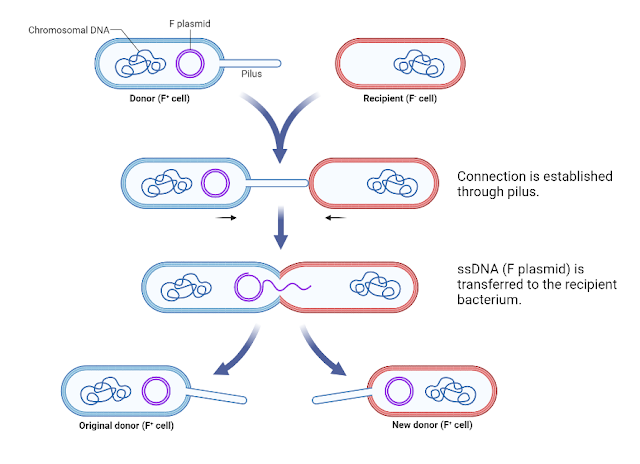
|
|
Conjugation in bacteria. Figure created in BioRender.com. |
Advantages of conjugation
Conjugation has some major advantages such as:
- New genetic combinations are produced that allow bacteria to survive in a particular environment. For example, the exchange of plasmid having antibiotics resistance genes will help the recipient bacterium to survive those particular antibiotics.
- This process allows the transfer of relatively large amounts of genetic material.
- As the connection is established through sex pili, minimum disruption of the cell envelope occurs.
Disadvantages of conjugation
Some disadvantages of the conjugation process include:
- This process requires the mating of donor and recipient bacteria.
- Environmental conditions affect the transfer of genetic material between two bacteria.
2. Transformation
It is a method of horizontal gene transfer in which bacteria take up genetic material (DNA) from their surrounding environment. The genetic material mostly comes from dead bacterial cells. Griffith originally mentioned it in Streptococcus pneumoniae in 1928.
This property of bacteria is used in DNA recombinant technology to make transgenic bacteria and obtain desired products. The steps involved in the transformation of bacteria include:
- The bacterium first recognizes and binds with the genetic material.
- The genetic material is transported inside the cell through the protein channels in the cell membrane.
- The foreign DNA is then incorporated into the DNA of bacteria.
Advantages of transformation
- This enables the horizontal transfer of adaptive features that are difficult for point mutations to obtain.
- It also allows the bacteria to attain antibiotic resistance.
3. Transduction
It is a recombination method that involves the transfer of genetic material from one bacterium to another through bacteriophage. Bacteriophage is a virus that infects the bacterium. The steps involved in transduction are:
- Bacteriophage lands on the surface of the bacterium and attaches itself to it.
- The viral genome is inserted into the bacterium.
- The viral genome hijacks bacterial machinery and replicates its DNA and produces proteins.
- The bacteriophage is assembled within the bacterium and also takes up some of the bacterial DNA.
- The bacterium cells bursts and new bacteriophages are released.
- These phages will then infect the other bacterium and previously taken bacterial DNA is inserted into the new bacterium which results in genetic recombination.

|
|
Bacterial DNA transduction. Figure created in BioRender.com |
Some questions and answers
1. How do bacteria reproduce asexually?
A. Bacteria reproduce asexually by the process of binary fission.
2. What are 3 ways bacteria produce genetic recombination?
A. The three ways bacteria produce genetic recombination include conjugation, transformation, and transduction.
3. What is the evolutionary advantage of conjugation?
A. New genetic combinations are produced that allow the bacteria to survive in a particular environment. For example, the exchange of plasmid having antibiotics resistance genes will help the recipient bacterium to survive those particular antibiotics.
4. What is the natural transformation in bacteria?
A. Natural transformation is a method of horizontal gene transfer in which bacteria take up genetic material (DNA) from their surrounding environment left by the other dead bacteria.
5. Which type of virus is involved in transduction?
A. Bacteriophage is a virus that infects the bacterium and is involved in the process of transduction.




0 Comments