What are Palindromic Nucleotide Sequence
The root word of "palindrome" is "palin" which comes from the Greek word "palin" meaning "again" or "back." The suffix "-drome" is also from Greek, and means "running." So, a palindrome is a sequence of letters, words or numbers that run the same way backward or forward.
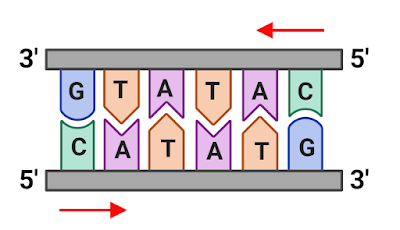
Palindromic nucleotide sequences are sequences of nucleotides (the building blocks of DNA and RNA) that read the same backwards as forwards. For example, the sequence "AGTGAT" is palindromic because it reads the same forward and backward (AGTGAT and TAGTGA).
|
|
Palindromic sequence is same backward and forward. |
Examples of Palindromic Sequences from Daily Life
Here are a few examples to understand the concept of palindromic sequences:
- "ABA"
- "RACECAR"
- "MADAM"
- "LEVEL"
- "ROTATOR"
- "REFER"
- "DEED"
These examples are of different types of palindromes:
- "ABA" is a palindrome of 3 words.
- "RACECAR" and "MADAM" are palindrome of word.
- "LEVEL" and "REFER" are palindrome of 5 letters.
- "ROTATOR" and "DEED" are palindrome of 6 letters.
They are same even if you read it from right side or left side.
Examples of palindromic sequences in genome
Here are a few examples of palindromic sequences found in DNA or RNA:
- "AGCTAGC" is a palindrome of a DNA sequence.
- "UACUUAC" is a palindrome of a RNA sequence
- "CAGTGAC" is a palindrome of a DNA sequence
- "AGGGAGGG" is a palindrome of a DNA sequence
- "GGCGCGG" is a palindrome of a DNA sequence
Palindromic Sequences Role in Restriction Enzyme Recognition Site
A restriction enzyme recognition site is a specific sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is recognized and cleaved by a specific restriction enzyme. Restriction enzymes, also known as restriction endonucleases, are enzymes that cut double-stranded DNA at specific locations, creating "sticky ends" or "cohesive ends" on the ends of the cut DNA. These sticky ends can then be used in molecular biology techniques such as DNA cloning and genome editing.
The recognition site of a restriction enzyme is typically a short sequence of 4-8 base pairs, and is often palindromic, meaning that the sequence reads the same in both directions. For example, the restriction enzyme EcoRI recognizes the sequence "GAATTC" and cuts the DNA between the G and A, creating the sticky ends "G" and "AATTC".
Video Lesson on What are Palindromic Nucelotide Sequence
Functions of Palindromic Sequences
They have been found to play a role in various molecular biology processes, including gene regulation and DNA repair. They are often found in the non-coding regions of DNA, such as promoters and enhancers, and are thought to play a role in the regulation of gene expression. Some specific examples of palindromic sequences include the TATA box and CCAAT box, which are found in the promoter regions of many genes and are involved in the regulation of transcription.
Additionally, many transcription factor binding sites, which are regions of DNA that bind to specific proteins and control gene expression, are also palindromic sequences.
Palindromic sequences can also be found in coding regions and may have implications in genetic disorders and disease.
Palindromic sequences have also been found to be involved in the protection of RNA molecules, by helping to stabilize their secondary structure.
In addition, palindromic sequences have been implicated in the development of cancer. Some oncogenes, which are genes that have the potential to cause cancer, have been found to contain palindromic sequences in their promoter regions. These sequences may help to increase the expression of oncogenes, leading to the uncontrolled cell growth that is characteristic of cancer.
In summary, Palindromic sequences have a role in molecular biology, RNA protection, and cancer, including gene regulation and DNA repair, stabilizing RNA molecules, and oncogene expression, as well as increase the risk of cancer when DNA repair genes are defective.
Some Questions and Answer
1. What is palindromic sequence?
A. Palindromic nucleotide sequences are sequences of nucleotides (the building blocks of DNA and RNA) that read the same backwards as forwards.
2. How is palindromic sequence related to restriction enzymes?
A. The recognition site of a restriction enzyme is typically a short sequence of 4-8 base pairs, and is often palindromic, meaning that the sequence reads the same in both directions. For example, the restriction enzyme EcoRI recognizes the sequence "GAATTC".
3. How palindromic sequences linked to cancer?
A. The mutations in DNA repair genes that lead to defects in the recognition and repair of palindromic sequences have been linked to an increased risk of cancer.





0 Comments