Define diffusion
Diffusion refers to the process by which particles, molecules, or other substances move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. This movement occurs in order to achieve a more uniform distribution of the substances.
Explanation of diffusion
The driving force behind diffusion is the tendency of particles to move down their concentration gradient, which is the gradual change in concentration across a space. In the absence of external forces, substances will naturally move from regions of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration until an equilibrium is reached, where the concentration is uniform throughout the system
Diffusion and its importance
The rate of diffusion is influenced by factors such as temperature, concentration gradient, particle size, and the nature of the medium through which the substances are diffusing. Diffusion plays a crucial role in various biological processes, such as the exchange of gases in the respiratory system, the movement of nutrients within cells, and the diffusion of chemicals across cell membranes. Additionally, diffusion has applications in fields such as chemistry, physics, and engineering.
Define osmosis
Osmosis is a specific type of diffusion that involves the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of higher water potential to an area of lower water potential. The goal of osmosis is to equalize the concentration of water molecules on both sides of the membrane.
The direction of water movement is determined by the water potential. This process is essential in biological systems, particularly in cells, where maintaining the proper balance of water and solutes is crucial for various physiological functions.
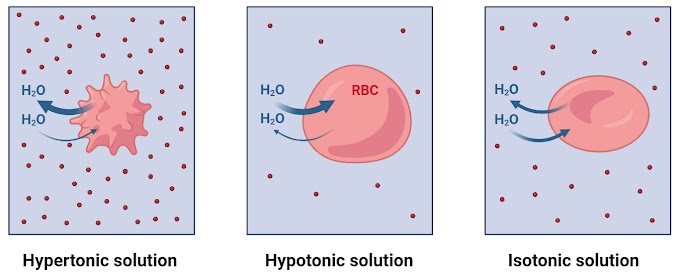
Three terms of osmosis
There are three main terms used to describe the relationship between the concentration of solutes and water movement in osmosis:
1. Isotonic
The water potential on both sides of the membrane are equal, resulting in no net movement of water.
2. Hypertonic
The solution has a lower water potential compared to the other side of the membrane. Water moves from the side with higher water potential to the side with lower water potential.
3. Hypotonic
The solution has a higher water potential compared to the other side of the membrane. Water moves from the side with lower water potential to the side with higher water potential.
Importance of osmosis
Osmosis is crucial for maintaining the proper balance of fluids in cells and organisms. It plays a vital role in processes such as nutrient uptake in plants, regulation of cell volume, and kidney function in animals.
Similarities and differences between diffusion and osmosis
Diffusion and osmosis are both fundamental processes that involve the movement of molecules across a concentration gradient, yet they exhibit key similarities and differences.
Similarities between diffusion and osmosis
Diffusion and osmosis share several similarities as they are both processes involving the movement of molecules. Here are some common similarities between diffusion and osmosis:
1. Passive processes
Both diffusion and osmosis are passive processes, meaning they do not require energy input from the cell or organism. The movement occurs spontaneously due to the concentration gradient.
2. Movement from high to low concentration
In both diffusion and osmosis, the direction of movement is from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. This movement continues until equilibrium is reached.
3. Influence of concentration gradient
The rate of diffusion and osmosis is influenced by the concentration gradient, with a more rapid movement occurring when there is a steeper difference in concentration.
4. Aimed at achieving equilibrium
The ultimate goal of both processes is to achieve equilibrium, where the concentration of solutes or particles is the same on both sides of the membrane. Once equilibrium is reached, there is no net movement of molecules.5. Affected by temperature
Both processes are influenced by temperature. Generally, an increase in temperature leads to a higher rate of diffusion and osmosis because it enhances the kinetic energy of the molecules.
6. Important in biological systems
Both diffusion and osmosis are critical processes in biological systems. They play essential roles in processes such as nutrient uptake, waste removal, and maintenance of cell and organismal homeostasis.
While diffusion is a broader term encompassing the movement of any type of particles, osmosis specifically refers to the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane. Despite their differences, these processes share fundamental principles and are integral to the functioning of living organisms.
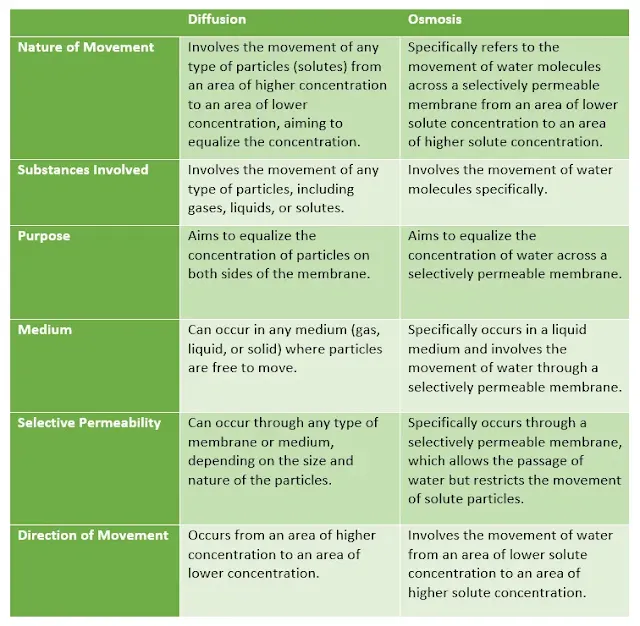
Differences between diffusion and osmosis
Diffusion and osmosis, while sharing similarities, also have distinct differences. Here are some key differences between diffusion and osmosis:
|
|
Diffusion |
Osmosis |
|
Nature of Movement |
Involves the movement of any type of particles (solutes) from an
area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration,
aiming to equalize the concentration. |
Specifically refers to the movement of water molecules across a
selectively permeable membrane from an area of lower solute
concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. |
|
Substances Involved |
Involves the movement of any type of particles, including gases,
liquids, or solutes. |
Involves the movement of water molecules specifically. |
|
Purpose |
Aims to equalize the concentration of particles on both sides of the
membrane.
|
Aims to equalize the concentration of water across a selectively
permeable membrane. |
|
Medium |
Can occur in any medium (gas, liquid, or solid) where particles are
free to move.
|
Specifically occurs in a liquid medium and involves the movement of
water through a selectively permeable membrane. |
|
Selective Permeability |
Can occur through any type of membrane or medium, depending on the
size and nature of the particles.
|
Specifically occurs through a selectively permeable membrane, which
allows the passage of water but restricts the movement of solute
particles. |
|
Direction of Movement |
Occurs from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower
concentration.
|
Involves the movement of water from an area of lower solute
concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. |
Example of diffusion
Imagine a room where someone opens a bottle of perfume. Initially, the fragrance is concentrated near the open bottle. As time passes, the perfume molecules start to spread throughout the room. This is an example of diffusion. The perfume molecules move from an area of higher concentration (near the open bottle) to an area of lower concentration (across the room). Eventually, the fragrance becomes evenly distributed, demonstrating the principle of diffusion.
Example of osmosis
Consider a scenario where you have a semi-permeable membrane separating two solutions: one with a high concentration of sugar molecules and another with a low concentration of sugar molecules. If the membrane allows the passage of water but not sugar molecules, osmosis will occur.
In this case, water molecules will move from the side with lower sugar concentration to the side with higher sugar concentration. The goal is to equalize the concentration of water on both sides of the membrane. This process is crucial in biological systems.
For instance, in plant cells, water moves into the cell through osmosis, causing the cell to swell and become turgid, which is important for maintaining cell structure and rigidity. In contrast, animal cells may experience osmotic effects such as cell shrinkage or swelling depending on the surrounding environment.
Some questions and answers
1. How do diffusion and osmosis differ in terms of the substances involved?
A: Diffusion involves the movement of any type of particles, while osmosis specifically refers to the movement of water molecules.2. What is the main purpose of diffusion, and how does it differ from the purpose of osmosis?
A: Diffusion aims to equalize the concentration of particles on both sides of the membrane, while osmosis aims to equalize the concentration of water across a selectively permeable membrane.
3. How does the medium in which diffusion and osmosis occur differ?
A: Diffusion can occur in any medium (gas, liquid, or solid), while osmosis specifically occurs in a liquid medium and involves the movement of water through a selectively permeable membrane.4. What role does selective permeability play in the differences between diffusion and osmosis?
A: While diffusion can occur through any type of membrane, osmosis specifically occurs through a selectively permeable membrane, allowing the passage of water but restricting the movement of solute particles.
5. What is the common purpose of diffusion and osmosis?
A: The common goal is to achieve equilibrium by moving substances from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration.
6. How are the rates of diffusion and osmosis influenced by the concentration gradient?
A: The rates of both processes are influenced by the concentration gradient, with more rapid movement occurring when there is a steeper difference in concentration.
7. In what way do diffusion and osmosis share a similarity in terms of movement direction?
A: Both processes involve movement from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
8. How do temperature changes affect both diffusion and osmosis?
A: An increase in temperature generally leads to a higher rate of diffusion and osmosis, as it enhances the kinetic energy of the molecules involved.




0 Comments