Understanding the principles of water potential and osmosis is fundamental to comprehending various biological processes, from cellular functioning to organismal survival.
Water, the universal solvent, plays a pivotal role in biological systems, where its movement across cellular membranes shapes cell structure, function, and overall homeostasis.
Water potential, a concept derived from thermodynamics, quantifies the tendency of water molecules to move from one area to another.
Osmosis, a specific type of diffusion involving water, underpins numerous physiological phenomena, including the regulation of cell volume, nutrient uptake in roots, and the functioning of kidney nephrons.
Water Potential and Osmosis Worksheet
Through water potential and osmosis worksheet, we aim to grasp the mechanisms governing water movement and its vital role in sustaining life processes.
1.
Define the term “water potential”.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
2. What is the relationship between osmosis and water potential?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
3. How does water potential affect the movement of water in plants?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
4. What are the factors that contribute to water potential?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
5. What would happen to a red blood cell placed in a hypertonic
solution?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
6. Match the description to the terms in other column.
|
Description |
Terms |
|
The movement of water molecules across a semipermeable
membrane |
Water potential |
|
The potential energy of water in a system compared to pure
water |
Solute potential |
|
The pressure exerted by the cell contents against the cell wall
in plant cells |
Osmosis |
|
A solution with equal solute concentration compared to another
solution |
Isotonic solution |
|
The effect of solute concentration on the movement of water
molecules |
Turgor pressure |
7. Imagine you have a container divided into two compartments by a
semipermeable membrane. In one compartment, there is a 10% salt solution,
and in the other compartment, there is distilled water. Predict what will
happen to the water level in each compartment over time.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
8. Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.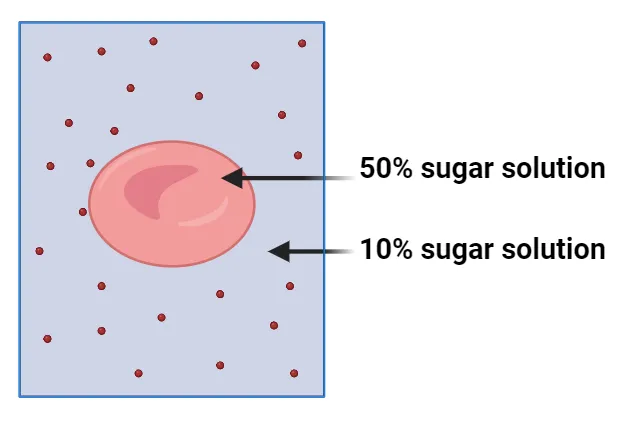
1. Identify the type of solution surrounding the cell:
hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
2. Predict the direction of water movement: into the cell, out of the
cell, or no net movement.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
3. Explain the potential consequences for the cell based on your
identification and prediction.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………






0 Comments